采用链式存储的栈成为链式栈(或简称链栈), 链栈的优点是便于多个栈共享存储空间和提高其效率, 且不存在栈满上溢的情况(因为链栈是靠指针链接到一起,只要内存够大, 则链栈理论上可以存储的元素是没有上限的);
与顺序栈相比, 由于顺序栈是采用的数组实现, 因此一旦数组填满, 则必须重新申请内存, 并将所有元素”搬家”, 而链栈则省略了这一”耗时耗力”的工作, 但却需要付出附加一个指针的代价;
链栈通常采用单链表实现, 并规定所有的操作都必须实在单链表的表头进行, 而且w我们的链栈没有头结点, m_top直接指向栈顶元素;
链式栈的图示如下:
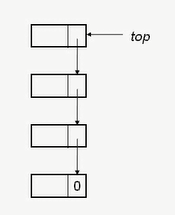
链栈节点构造:
template <typename Type>
class ChainNode
{
template <typename T>
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const LinkStack<T> &stack);
friend class LinkStack<Type>;
private:
ChainNode(const Type &_data, ChainNode *_next = NULL)
:data(_data), next(_next) {}
Type data;
ChainNode *next;
};
链栈设计:
template <typename Type>
class LinkStack
{
template <typename T>
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const LinkStack<T> &stack);
public:
LinkStack(): m_top(NULL) {}
~LinkStack()
{
makeEmpty();
}
bool isEmpty() const
{
return m_top == NULL;
}
void pop() throw(std::out_of_range);
const Type &top() const throw(std::out_of_range);
void push(const Type &data);
void makeEmpty();
private:
ChainNode<Type> *m_top;
};
栈的三大操作:
template <typename Type>
const Type &LinkStack<Type>::top() const
throw (std::out_of_range)
{
if (isEmpty())
throw std::out_of_range("stack is empty, can`t get data");
return m_top->data;
}
template <typename Type>
void LinkStack<Type>::pop()
throw (std::out_of_range)
{
if (isEmpty())
throw std::out_of_range("stack is empty, can`t delete");
ChainNode<Type> *deleteNode = m_top;
m_top = m_top->next;
delete deleteNode;
}
template <typename Type>
void LinkStack<Type>::push(const Type &data)
{
//此处是整个链栈的关键点
// 该操作会生成一个节点,
// 并自动将m_top上移一格,
// 而且将m_top原先指向的节点, 作为新生成的节点的下一节点
//注意此处
//如果第一次运行push, 则原m_top为NULL
// 新m_top指向第一个元素
m_top = new ChainNode<Type>(data, m_top);
}
清空整个栈:
template <typename Type>
void LinkStack<Type>::makeEmpty()
{
while (!isEmpty())
{
pop();
}
}
输出栈内所有内容:
template <typename Type>
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const LinkStack<Type> &stack)
{
ChainNode<Type> *currentNode = stack.m_top;
while (currentNode != NULL)
{
cout << currentNode->data << ' ';
currentNode = currentNode->next;
}
return os;
}
测试代码:
int main()
{
LinkStack<int> test;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
test.push(rand()%100);
}
cout << test << endl;
cout << "top = " << test.top() << endl;
test.pop();
cout << "top = " << test.top() << endl;
test.push(1);
cout << "top = " << test.top() << endl;
while (!test.isEmpty())
{
test.pop();
}
cout << test << endl;
test.push(11);
test.push(22);
test.push(33);
cout << test << endl;
test.makeEmpty();
try
{
cout << "top = " << test.top() << endl;
}
catch (const std::exception &e)
{
cerr << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
